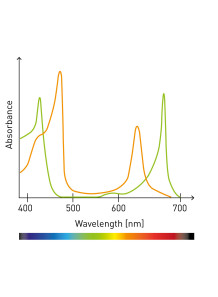
Peptide Purity Analysis (HPLC, includes reference material)
- Product Code: 35496
Peptide Purity Analysis using HPLC
Equipment and Reagents:
HPLC system (consisting of pumps, injector, column, detector, and integrator or data analysis software)
HPLC-grade solvents (e.g., water, acetonitrile, trifluoroacetic acid (TFA))
Analytical column suitable for peptide separation (e.g., C18 column)
Mobile phase (commonly used is a gradient of water/acetonitrile with TFA)
Peptide sample to be analyzed
Calibration standards (optional, for quantitative analysis)
HPLC vials and caps
Micropipettes and tips
Procedure:
Column Equilibration:
Prime the HPLC system with the mobile phase.
Equilibrate the column with the mobile phase according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Typically, this involves running a gradient of solvent A (e.g., water with TFA) and solvent B (e.g., acetonitrile with TFA) to achieve column equilibration.
Sample Preparation:
Prepare the peptide sample solution in a suitable solvent. Common solvents include water, acetonitrile, or a mixture of both, depending on the peptide's solubility.
Filter the sample solution through a 0.22 μm membrane filter to remove particulate matter that could clog the HPLC column.
Injection:
Inject an appropriate volume of the filtered peptide sample solution into the HPLC system using an autosampler or manual injector. The injection volume depends on the sensitivity of the detector and the concentration of the sample.
Gradient Elution:
Run a gradient elution program using the mobile phase. A typical gradient may start with a higher percentage of solvent A (e.g., 95%) and gradually increase solvent B over time. The exact gradient profile depends on the characteristics of the peptide being analyzed.
Monitor the eluent using a suitable detector, such as a UV-Vis detector at a wavelength appropriate for detecting peptides (e.g., 214 nm).
Data Collection and Analysis:
Collect chromatographic data using an integrator or data analysis software connected to the HPLC system.
Analyze the chromatogram to determine the retention time of the peptide peak(s) and the baseline separation from any impurities or other peaks.
Calculate the percentage purity of the peptide based on the area under the curve (AUC) of the main peptide peak(s) relative to the total AUC of all peaks in the chromatogram.
| Step | Procedure | Expected Result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| There is no item to display. | |||||
Peptide Purity Analysis using HPLC
Equipment and Reagents:
HPLC system (consisting of pumps, injector, column, detector, and integrator or data analysis software)
HPLC-grade solvents (e.g., water, acetonitrile, trifluoroacetic acid (TFA))
Analytical column suitable for peptide separation (e.g., C18 column)
Mobile phase (commonly used is a gradient of water/acetonitrile with TFA)
Peptide sample to be analyzed
Calibration standards (optional, for quantitative analysis)
HPLC vials and caps
Micropipettes and tips
Procedure:
Column Equilibration:
Prime the HPLC system with the mobile phase.
Equilibrate the column with the mobile phase according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Typically, this involves running a gradient of solvent A (e.g., water with TFA) and solvent B (e.g., acetonitrile with TFA) to achieve column equilibration.
Sample Preparation:
Prepare the peptide sample solution in a suitable solvent. Common solvents include water, acetonitrile, or a mixture of both, depending on the peptide's solubility.
Filter the sample solution through a 0.22 μm membrane filter to remove particulate matter that could clog the HPLC column.
Injection:
Inject an appropriate volume of the filtered peptide sample solution into the HPLC system using an autosampler or manual injector. The injection volume depends on the sensitivity of the detector and the concentration of the sample.
Gradient Elution:
Run a gradient elution program using the mobile phase. A typical gradient may start with a higher percentage of solvent A (e.g., 95%) and gradually increase solvent B over time. The exact gradient profile depends on the characteristics of the peptide being analyzed.
Monitor the eluent using a suitable detector, such as a UV-Vis detector at a wavelength appropriate for detecting peptides (e.g., 214 nm).
Data Collection and Analysis:
Collect chromatographic data using an integrator or data analysis software connected to the HPLC system.
Analyze the chromatogram to determine the retention time of the peptide peak(s) and the baseline separation from any impurities or other peaks.
Calculate the percentage purity of the peptide based on the area under the curve (AUC) of the main peptide peak(s) relative to the total AUC of all peaks in the chromatogram.
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |
Cart
No products