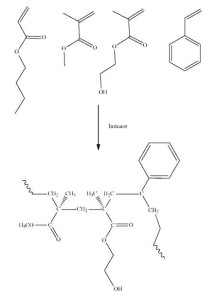
Acrylic polyol (OH 50, Tg 70C, Solid)
- Product Code: 35857
a type of polyol used in the production of polyurethane and other polymeric materials. It is derived from acrylic monomers and is notable for its excellent weather resistance, chemical resistance, and durability
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
Acrylic polyol is a type of polyol used in the production of polyurethane and other polymeric materials. It is derived from acrylic monomers and is notable for its excellent weather resistance, chemical resistance, and durability. Here are some key points about acrylic polyol:
Composition and Production
- Acrylic Monomers: Acrylic polyols are synthesized from acrylic monomers like acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, and their esters.
- Polymerization: These monomers undergo polymerization to form polyacrylic backbones with hydroxyl functional groups.
- Hydroxyl Groups: The presence of hydroxyl groups (-OH) in the polymer structure makes them reactive with isocyanates to form polyurethanes.
Properties
- Weather Resistance: Excellent resistance to UV radiation and environmental factors.
- Chemical Resistance: High resistance to solvents, acids, and alkalis.
- Durability: Provides long-lasting performance in harsh conditions.
- Flexibility: Offers good flexibility and adhesion properties.
Applications
-
Coatings:
- Automotive Coatings: Used in high-performance automotive topcoats for their gloss, durability, and resistance to weathering.
- Industrial Coatings: Employed in protective coatings for metal, wood, and plastic surfaces.
- Architectural Coatings: Utilized in exterior paints and finishes that require long-term resistance to environmental exposure.
-
Adhesives and Sealants:
- Construction Adhesives: Used in building materials for their strong bonding and resistance to environmental factors.
- Sealants: Provides flexible and durable sealing solutions for various applications.
-
Polyurethane Production:
- Flexible Foams: Used in the production of flexible polyurethane foams for furniture, bedding, and automotive interiors.
- Rigid Foams: Contributes to rigid foams used in insulation and structural applications.
- Elastomers: Forms the base for elastomeric materials that require both flexibility and durability.
Advantages
- Performance: High-performance properties suitable for demanding applications.
- Versatility: Can be formulated to meet specific application requirements.
- Environmental Resistance: Provides superior resistance to weathering and chemicals compared to other polyols.
- Aesthetic Quality: Produces high-gloss, clear, and durable finishes.
Disadvantages
- Cost: Typically more expensive than other types of polyols, such as polyester polyols.
- Processing Requirements: May require specific processing conditions and equipment to achieve desired properties.
Be the first to review this product :-)
Recommend Lab-Service
| Lab Service | Price |
|---|
a type of polyol used in the production of polyurethane and other polymeric materials. It is derived from acrylic monomers and is notable for its excellent weather resistance, chemical resistance, and durability
Acrylic polyol is a type of polyol used in the production of polyurethane and other polymeric materials. It is derived from acrylic monomers and is notable for its excellent weather resistance, chemical resistance, and durability. Here are some key points about acrylic polyol:
Composition and Production
- Acrylic Monomers: Acrylic polyols are synthesized from acrylic monomers like acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, and their esters.
- Polymerization: These monomers undergo polymerization to form polyacrylic backbones with hydroxyl functional groups.
- Hydroxyl Groups: The presence of hydroxyl groups (-OH) in the polymer structure makes them reactive with isocyanates to form polyurethanes.
Properties
- Weather Resistance: Excellent resistance to UV radiation and environmental factors.
- Chemical Resistance: High resistance to solvents, acids, and alkalis.
- Durability: Provides long-lasting performance in harsh conditions.
- Flexibility: Offers good flexibility and adhesion properties.
Applications
-
Coatings:
- Automotive Coatings: Used in high-performance automotive topcoats for their gloss, durability, and resistance to weathering.
- Industrial Coatings: Employed in protective coatings for metal, wood, and plastic surfaces.
- Architectural Coatings: Utilized in exterior paints and finishes that require long-term resistance to environmental exposure.
-
Adhesives and Sealants:
- Construction Adhesives: Used in building materials for their strong bonding and resistance to environmental factors.
- Sealants: Provides flexible and durable sealing solutions for various applications.
-
Polyurethane Production:
- Flexible Foams: Used in the production of flexible polyurethane foams for furniture, bedding, and automotive interiors.
- Rigid Foams: Contributes to rigid foams used in insulation and structural applications.
- Elastomers: Forms the base for elastomeric materials that require both flexibility and durability.
Advantages
- Performance: High-performance properties suitable for demanding applications.
- Versatility: Can be formulated to meet specific application requirements.
- Environmental Resistance: Provides superior resistance to weathering and chemicals compared to other polyols.
- Aesthetic Quality: Produces high-gloss, clear, and durable finishes.
Disadvantages
- Cost: Typically more expensive than other types of polyols, such as polyester polyols.
- Processing Requirements: May require specific processing conditions and equipment to achieve desired properties.
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |
Cart
No products