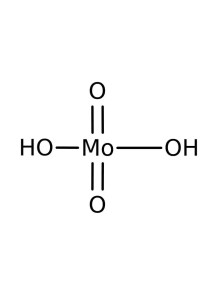
Ammonium Molybdate 98%
- Product Code: 36020
widely used chemical compound in agriculture, particularly for its role in plant nutrition
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
Ammonium molybdate is a widely used chemical compound in agriculture, particularly for its role in plant nutrition. Here is an overview of its properties, uses, and benefits:
Properties of Ammonium Molybdate:
- Chemical Composition: Ammonium molybdate typically refers to compounds like ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH₄)₆Mo₇O₂₄·4H₂O).
- Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, making it easy to apply as a foliar spray or soil amendment.
Role in Plant Nutrition:
- Essential Micronutrient: Molybdenum (Mo) is an essential micronutrient for plants. Although required in small amounts, it is crucial for various physiological functions.
- Enzyme Activation: Molybdenum is a key component of several plant enzymes, including nitrate reductase and nitrogenase, which are involved in nitrogen metabolism and fixation.
Benefits of Ammonium Molybdate in Plants:
- Nitrogen Fixation: In legumes, molybdenum is essential for nitrogen fixation, a process where atmospheric nitrogen is converted into a form usable by plants. It is vital for the symbiotic relationship between legumes and Rhizobium bacteria in root nodules.
- Nitrate Reduction: Molybdenum is involved in the conversion of nitrate to ammonia within the plant. This is a crucial step in nitrogen assimilation, influencing plant growth and protein synthesis.
- Enhanced Growth: Adequate molybdenum levels support overall plant health, leading to improved growth, better crop yields, and higher quality produce.
- Disease Resistance: Molybdenum can improve a plant's resistance to certain diseases by promoting robust growth and enhancing the plant's defense mechanisms.
Application of Ammonium Molybdate:
- Soil Application: Ammonium molybdate can be applied directly to the soil, particularly in areas where molybdenum deficiencies are common. This method ensures that the nutrient is available to plant roots.
- Foliar Spray: It can be applied as a foliar spray, allowing for quick uptake by the plant leaves. This method is useful for correcting deficiencies rapidly.
- Seed Treatment: Coating seeds with ammonium molybdate before planting can ensure adequate molybdenum supply right from germination, promoting healthy seedling growth.
Be the first to review this product :-)
Recommend Lab-Service
| Lab Service | Price |
|---|
Ammonium Molybdate 98%

widely used chemical compound in agriculture, particularly for its role in plant nutrition
Ammonium molybdate is a widely used chemical compound in agriculture, particularly for its role in plant nutrition. Here is an overview of its properties, uses, and benefits:
Properties of Ammonium Molybdate:
- Chemical Composition: Ammonium molybdate typically refers to compounds like ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH₄)₆Mo₇O₂₄·4H₂O).
- Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, making it easy to apply as a foliar spray or soil amendment.
Role in Plant Nutrition:
- Essential Micronutrient: Molybdenum (Mo) is an essential micronutrient for plants. Although required in small amounts, it is crucial for various physiological functions.
- Enzyme Activation: Molybdenum is a key component of several plant enzymes, including nitrate reductase and nitrogenase, which are involved in nitrogen metabolism and fixation.
Benefits of Ammonium Molybdate in Plants:
- Nitrogen Fixation: In legumes, molybdenum is essential for nitrogen fixation, a process where atmospheric nitrogen is converted into a form usable by plants. It is vital for the symbiotic relationship between legumes and Rhizobium bacteria in root nodules.
- Nitrate Reduction: Molybdenum is involved in the conversion of nitrate to ammonia within the plant. This is a crucial step in nitrogen assimilation, influencing plant growth and protein synthesis.
- Enhanced Growth: Adequate molybdenum levels support overall plant health, leading to improved growth, better crop yields, and higher quality produce.
- Disease Resistance: Molybdenum can improve a plant's resistance to certain diseases by promoting robust growth and enhancing the plant's defense mechanisms.
Application of Ammonium Molybdate:
- Soil Application: Ammonium molybdate can be applied directly to the soil, particularly in areas where molybdenum deficiencies are common. This method ensures that the nutrient is available to plant roots.
- Foliar Spray: It can be applied as a foliar spray, allowing for quick uptake by the plant leaves. This method is useful for correcting deficiencies rapidly.
- Seed Treatment: Coating seeds with ammonium molybdate before planting can ensure adequate molybdenum supply right from germination, promoting healthy seedling growth.
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |
Cart
No products
Subtotal:
฿0.00
฿0.00
Total :