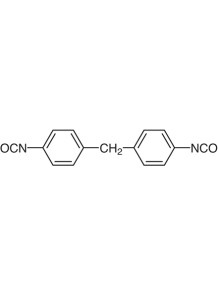
MDI (200mpa.s., NCO 31%, Function 2.6)
- Product Code: 35150
Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate, which is commonly used in the production of polyurethane (PU)
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
MDI stands for Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate, which is commonly used in the production of polyurethane (PU). In PU curing, MDI serves as one of the key components in the reaction that forms the polymer structure of polyurethane.
Polyurethane curing typically involves the reaction of MDI with polyols or other compounds containing hydroxyl groups, which leads to the formation of urethane linkages. This reaction can occur in various processes such as casting, molding, spraying, or foaming, depending on the desired properties and applications of the final polyurethane product.
The curing process usually involves controlling factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of catalysts or additives to achieve the desired properties of the cured polyurethane. MDI's reactivity and compatibility with other components make it a widely used isocyanate in the polyurethane industry for various applications ranging from insulation, adhesives, coatings, to foams.
Be the first to review this product :-)
Recommend Lab-Service
| Lab Service | Price |
|---|

Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate, which is commonly used in the production of polyurethane (PU)
MDI stands for Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate, which is commonly used in the production of polyurethane (PU). In PU curing, MDI serves as one of the key components in the reaction that forms the polymer structure of polyurethane.
Polyurethane curing typically involves the reaction of MDI with polyols or other compounds containing hydroxyl groups, which leads to the formation of urethane linkages. This reaction can occur in various processes such as casting, molding, spraying, or foaming, depending on the desired properties and applications of the final polyurethane product.
The curing process usually involves controlling factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of catalysts or additives to achieve the desired properties of the cured polyurethane. MDI's reactivity and compatibility with other components make it a widely used isocyanate in the polyurethane industry for various applications ranging from insulation, adhesives, coatings, to foams.
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |
Cart
No products