Intestine Absorption (Franz Cell, Porcine Intestine, Krebs-Ringer, 1 Time Point)
- Product Code: 125440
Intestine permeability analysis service with Franz Cell using porcine small intestine with Krebs-Ringer HEPES buffer.
description Service Overview
Intestine Absorption (Franz Cell, Porcine Intestine, Krebs-Ringer)
Materials Needed:
- Franz diffusion cells
- Porcine intestine (fresh or properly stored)
- Krebs-Ringer buffer (either HEPES or sodium bicarbonate-buffered, depending on setup)
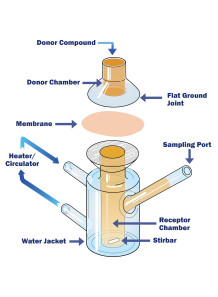
- Donor and receptor compartments for Franz cells
- Magnetic stirrers
- Syringes and needles
- pH meter
- Incubator or water bath (if needed for maintaining temperature)
- Analytical instruments (e.g., HPLC, spectrophotometer) for sample analysis
- Absorption compound (test substance)
Preparation:
-
Prepare Krebs-Ringer Buffer:
- For HEPES-buffered: Dissolve the appropriate amounts of NaCl, KCl, CaCl₂, MgSO₄, NaH₂PO₄, glucose, and HEPES in distilled water. Adjust pH to 7.4.
- For sodium bicarbonate-buffered: Prepare similarly but use NaHCO₃ instead of HEPES, and adjust pH with a CO₂ environment if necessary.
-
Prepare Porcine Intestine:
- Obtain fresh porcine intestines from a suitable source.
- Clean the intestine to remove any contents and mucosal debris.
- Cut the intestine into appropriate sections for mounting on the Franz cell.
-
Mount the Intestinal Tissue:
- Carefully mount a section of the intestine between the donor and receptor compartments of the Franz cell. Ensure no leaks and that the tissue is securely in place.
Experiment Setup:
-
Fill Receptor Compartment:
- Fill the receptor compartment with the Krebs-Ringer buffer, ensuring that it is well-mixed and aerated. This compartment will mimic the blood side of the intestine.
- Place a magnetic stir bar in the receptor compartment for continuous mixing.
-
Add Test Compound to Donor Compartment:
- Apply the test compound (the substance you want to study for absorption) to the donor compartment. This compartment represents the lumen side of the intestine.
- The compound should be in a suitable solvent or vehicle that does not damage the tissue.
-
Maintain Experimental Conditions:
- Place the Franz cells in an incubator or water bath to maintain physiological temperature (usually around 37°C).
- Ensure continuous stirring of the receptor compartment to simulate blood flow and to prevent boundary layer formation.
Sampling:
-
Sample Collection:
- At predetermined time intervals (e.g., every 30 minutes or hourly), withdraw small aliquots from the receptor compartment using a syringe.
- Replace the withdrawn volume with fresh Krebs-Ringer buffer to maintain constant volume.
-
Analyze Samples:
- Analyze the collected samples using appropriate analytical techniques (e.g., HPLC, UV-spectrophotometry) to determine the concentration of the test compound.
- Plot the concentration of the test compound in the receptor compartment over time to assess the absorption rate.
timeline Service Steps
| Step | Procedure | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|
| info Service steps will be provided upon request | ||