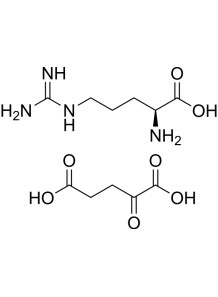
L-Arginine Alpha-Ketoglutarate (AAKG, 2:1)
- Product Code: 34090
supplement that combines the amino acid L-arginine with alpha-ketoglutarate, a compound involved in the Krebs cycle, a series of chemical reactions that occur in the cells to generate energy
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
| Test Name | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White to yellow crystalline powder |
| Assay | 98-102% |
| L-Arginine | 65.5-69.0% |
| Alpha Ketoglutarate | 26.5-29.0% |
| Specific Rotation [a]D20(8g/100ml,6N HCL) | +16.5 to +18.5 degree |
| pH (10% in water) | 5.5-7.0 |
| Water Content | 6.8% Max |
| Chloride | 0.05% Max |
| Loss on drying | 1.0% Max |
| Residue on ignition | 0.2% Max |
| Heavy metals | 10ppm Max |
| As | 1ppm Max |
| Pb | 1ppm Max |
| Cd | 1ppm Max |
| Hg | 0.1ppm Max |
| Iron (ppm) | 10ppm Max |
| Bulk density (g/ml) | 0.5 Min |
| Particle size | 99% pass 30 Mesh |
| Total plate count | 1000CFU/g Max |
| Yeast | 100CFU/g Max |
| Mold | 100CFU/g Max |
| E.Coli | Negative |
| Salmonella | Negative |
| Staphylococcus Aureus | Negative |
| Melamine and Melamine derivatives | Negative |
L-Arginine Alpha-Ketoglutarate (AAKG, 2:1) is a compound formed by combining two molecules of the amino acid L‑arginine with one molecule of alpha‑ketoglutarate. It’s commonly marketed in sports nutrition for its potential to support nitric oxide production and, by extension, enhance blood flow, exercise performance, and recovery. Below is an overview of its purported benefits along with examples from research studies.
1. Enhanced Nitric Oxide Production & Vascular Function
Mechanism:
- L‑Arginine as a Precursor: L‑arginine is a substrate for nitric oxide synthase, the enzyme that produces nitric oxide (NO). Increased NO can promote vasodilation, improving blood flow to muscles and other tissues.
Research Example: - Reviews on nitric oxide have highlighted the role of L‑arginine supplementation in promoting vascular function, which is a key rationale behind using AAKG in athletic and cardiovascular contexts.
2. Exercise Performance & Recovery
Proposed Benefits:
- Muscle Pump & Endurance: Improved blood flow may help deliver oxygen and nutrients more efficiently during exercise.
- Recovery Support: By enhancing nutrient delivery, AAKG is thought to aid in post‐exercise recovery.
Research Findings: - Some studies have examined whether AAKG supplementation can boost anaerobic performance and reduce fatigue. For instance, a study by Pérez‑Guisado and Jakeman evaluated the acute effects of AAKG on strength performance, reporting mixed results that suggest benefits may be modest or vary among individuals.
3. Cardiovascular Health
Potential Impact:
- Blood Pressure & Vascular Health: Through enhanced NO production, AAKG might help in maintaining healthy blood pressure and supporting overall cardiovascular function.
Research Context: - While there is a physiological basis for these benefits, clinical studies have produced inconsistent results, and more targeted research is needed to establish clear cardiovascular advantages from AAKG specifically.
Be the first to review this product :-)
Recommend Lab-Service
| Lab Service | Price |
|---|
supplement that combines the amino acid L-arginine with alpha-ketoglutarate, a compound involved in the Krebs cycle, a series of chemical reactions that occur in the cells to generate energy
L-Arginine Alpha-Ketoglutarate (AAKG, 2:1) is a compound formed by combining two molecules of the amino acid L‑arginine with one molecule of alpha‑ketoglutarate. It’s commonly marketed in sports nutrition for its potential to support nitric oxide production and, by extension, enhance blood flow, exercise performance, and recovery. Below is an overview of its purported benefits along with examples from research studies.
1. Enhanced Nitric Oxide Production & Vascular Function
Mechanism:
- L‑Arginine as a Precursor: L‑arginine is a substrate for nitric oxide synthase, the enzyme that produces nitric oxide (NO). Increased NO can promote vasodilation, improving blood flow to muscles and other tissues.
Research Example: - Reviews on nitric oxide have highlighted the role of L‑arginine supplementation in promoting vascular function, which is a key rationale behind using AAKG in athletic and cardiovascular contexts.
2. Exercise Performance & Recovery
Proposed Benefits:
- Muscle Pump & Endurance: Improved blood flow may help deliver oxygen and nutrients more efficiently during exercise.
- Recovery Support: By enhancing nutrient delivery, AAKG is thought to aid in post‐exercise recovery.
Research Findings: - Some studies have examined whether AAKG supplementation can boost anaerobic performance and reduce fatigue. For instance, a study by Pérez‑Guisado and Jakeman evaluated the acute effects of AAKG on strength performance, reporting mixed results that suggest benefits may be modest or vary among individuals.
3. Cardiovascular Health
Potential Impact:
- Blood Pressure & Vascular Health: Through enhanced NO production, AAKG might help in maintaining healthy blood pressure and supporting overall cardiovascular function.
Research Context: - While there is a physiological basis for these benefits, clinical studies have produced inconsistent results, and more targeted research is needed to establish clear cardiovascular advantages from AAKG specifically.
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |
Cart
No products