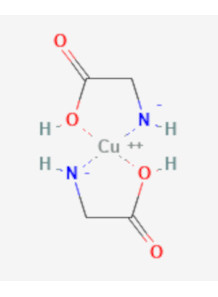
Copper Glycinate (14% Copper)
- Product Code: 31466
chelate of copper which copper binds to the amino acid glycine Copper is an essential mineral that plays an important role in many physiological processes in the body.
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
| Test Name | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Blue powder/crystalline |
| Copper Content w/% | 28% Min |
| Loss on drying (%) | 8 Max |
| pH | 7-9 |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) | 15ppm Max |
| Arsenic | 1ppm Max |
Copper glycinate is the chelated form of copper. which copper binds to the amino acid glycine Copper is an essential mineral that plays an important role in various physiological processes in the body.
Antioxidant activity: Copper is involved in the production of antioxidant enzymes that protect cells from free radical damage caused by free radicals. by neutralizing these harmful molecules Copper contributes to the overall antioxidant protection in the body.
Iron Metabolism: Copper is essential for the absorption, transport and utilization of iron. It plays a role in red blood cell formation and ensures proper iron levels. Prevent conditions such as iron deficiency anemia.
Connective tissue formation: Copper is involved in the synthesis of collagen and elastin. These are two essential proteins that provide strength, structure and elasticity to connective tissues such as skin, tendons and blood vessels. Adequate levels of copper are essential for maintaining healthy connective tissue.
Nervous system function: Copper plays a role in the development and maintenance of the nervous system. contributes to the production of neurotransmitters and myelin which is a protective coating around nerve fibers Copper deficiency can affect nervous system function.
Supports the immune system: Copper is involved in the functioning of the immune system. Helps in the production and activation of immune cells Contributes to a strong immune system against pathogens
Be the first to review this product :-)
Recommend Lab-Service
| Lab Service | Price |
|---|
chelate of copper which copper binds to the amino acid glycine Copper is an essential mineral that plays an important role in many physiological processes in the body.
Copper glycinate is the chelated form of copper. which copper binds to the amino acid glycine Copper is an essential mineral that plays an important role in various physiological processes in the body.
Antioxidant activity: Copper is involved in the production of antioxidant enzymes that protect cells from free radical damage caused by free radicals. by neutralizing these harmful molecules Copper contributes to the overall antioxidant protection in the body.
Iron Metabolism: Copper is essential for the absorption, transport and utilization of iron. It plays a role in red blood cell formation and ensures proper iron levels. Prevent conditions such as iron deficiency anemia.
Connective tissue formation: Copper is involved in the synthesis of collagen and elastin. These are two essential proteins that provide strength, structure and elasticity to connective tissues such as skin, tendons and blood vessels. Adequate levels of copper are essential for maintaining healthy connective tissue.
Nervous system function: Copper plays a role in the development and maintenance of the nervous system. contributes to the production of neurotransmitters and myelin which is a protective coating around nerve fibers Copper deficiency can affect nervous system function.
Supports the immune system: Copper is involved in the functioning of the immune system. Helps in the production and activation of immune cells Contributes to a strong immune system against pathogens
| Mechanism | - |
| Appearance | - |
| Longevity | - |
| Strength | - |
| Storage | - |
| Shelf Life | - |
| Allergen(s) | - |
| Dosage (Range) | - |
| Recommended Dosage | - |
| Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Recommended Dosage (Per Day) | - |
| Mix Method | - |
| Heat Resistance | - |
| Stable in pH range | - |
| Solubility | - |
| Product Types | - |
| INCI | - |
Cart
No products